Read the full article on DataCamp: DeepSeek-R1 RAG Chatbot With Chroma, Ollama, and Gradio
Learn how to build a local Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) chatbot using DeepSeek-R1 with Ollama, LangChain, and Chroma.
Overview
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has emerged as a powerful approach for building AI applications that generate precise, grounded, and contextually relevant answers by retrieving and synthesizing knowledge from external sources.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn step-by-step how to build a RAG-based chatbot using DeepSeek-R1 and a book on the foundations of LLMs as the knowledge base. By the end of this tutorial, you will be able to create a local RAG application capable of answering questions from the book and interacting with users via a Gradio interface.
Why Use DeepSeek-R1 With RAG?
DeepSeek-R1 is an ideal fit for RAG-based systems due to its optimized performance, advanced vector search capabilities, and flexibility across different environments, from local setups to scalable deployments. Here are some reasons why it’s effective:
- High-performance retrieval: DeepSeek-R1 handles large document collections with low latency.
- Fine-grained relevance ranking: It ensures accurate retrieval of passages by computing semantic similarity.
- Cost and privacy benefits: You can run DeepSeek-R1 locally to avoid API fees and keep sensitive data secure.
- Easy integration: It easily integrates with vector databases like Chroma.
- Offline capabilities: With DeepSeek-R1, you can build retrieval systems that work even without internet access once the model is downloaded.
Overview: Building a RAG Chatbot With DeepSeek-R1
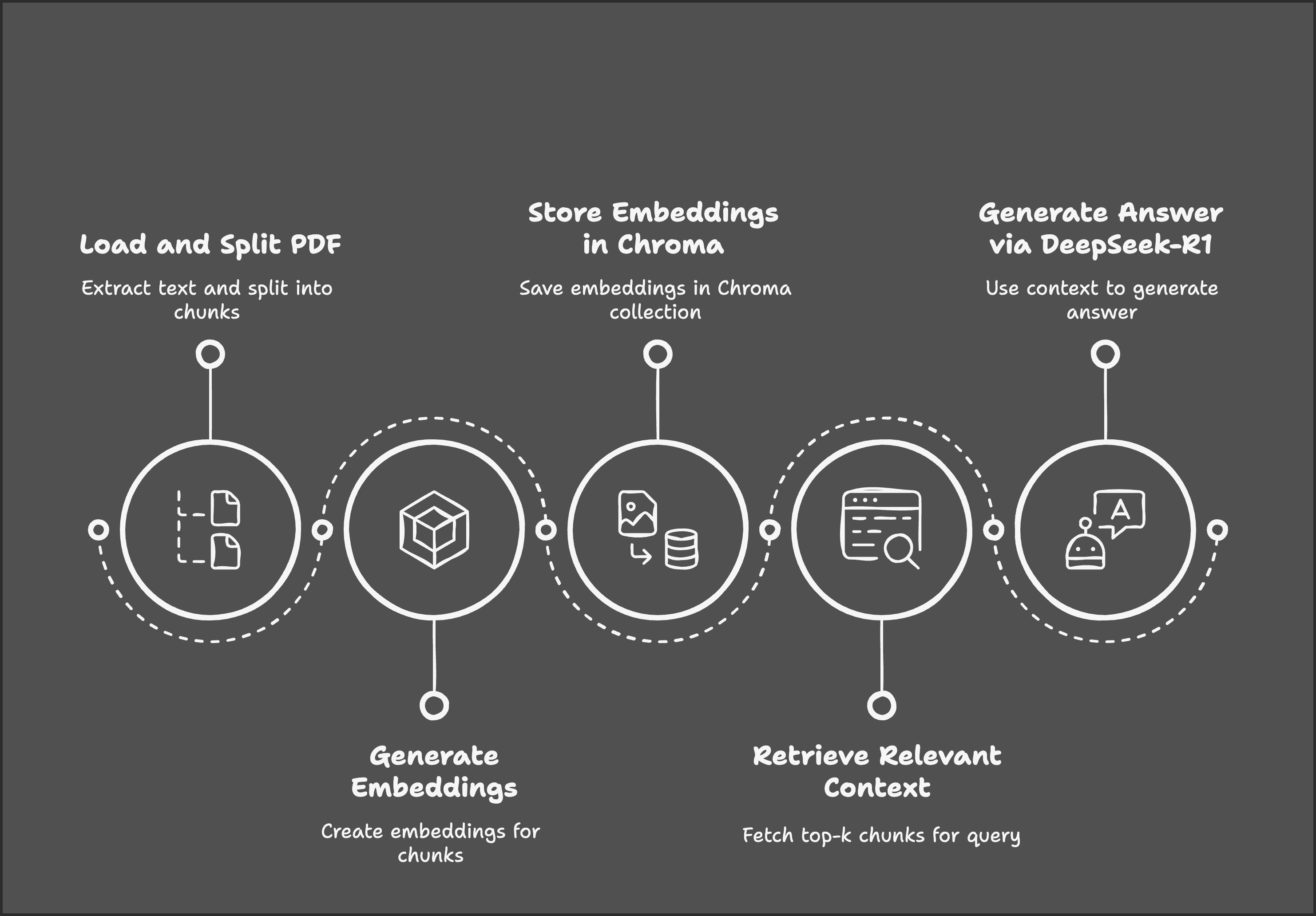
Our demo project focuses on building a RAG chatbot using DeepSeek-R1 and Gradio. The process begins with loading and splitting a PDF into text chunks, followed by generating embeddings for those chunks. These embeddings are stored in a Chroma database for efficient retrieval. When a user submits a query, the system retrieves the most relevant text chunks and uses DeepSeek-R1 to generate an answer based on the retrieved context.
Step-by-Step Implementation
Step 1: Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have the necessary tools and libraries installed, including Python 3.8+, LangChain, ChromaDB, and Gradio.
Step 2: Load the PDF Using PyMuPDFLoader
Use LangChain’s PyMuPDFLoader to extract text from the PDF version of the book Foundations of LLMs. This book is math-heavy, making it an excellent test case for the chatbot’s ability to explain complex concepts.
Step 3: Split the Document Into Smaller Chunks
Split the extracted text into smaller, overlapping chunks for better context retrieval. This step ensures that the system can efficiently process and retrieve relevant information.
Step 4: Generate Embeddings Using DeepSeek-R1
Use Ollama Embeddings based on DeepSeek-R1 to generate document embeddings. This step converts text chunks into high-dimensional vectors for efficient retrieval.
Step 5: Store Embeddings in Chroma Vector Store
Store the embeddings and corresponding text chunks in Chroma, a high-performance vector database. This setup ensures efficient retrieval of relevant document chunks during query processing.
Step 6: Initialize the Retriever
Initialize the Chroma retriever to use the same DeepSeek-R1 embeddings for queries. This step connects the retriever to the document collection for context-aware responses.
Step 7: Define the RAG Pipeline
Retrieve the most relevant chunks of text and format them for DeepSeek-R1 to generate answers. This step combines the retrieved content into a single context string for further processing.
Step 8: Query DeepSeek-R1 for Contextual Answers
Send the user’s question and retrieved context to DeepSeek-R1 via Ollama to generate a final answer. This step ensures that the chatbot provides accurate and contextually relevant responses.
Step 9: Build the Gradio Interface
Use Gradio to create an interactive interface for users to ask questions related to the knowledge base. This step enables seamless interaction with the chatbot.
Optimizations
The basic implementation of RAG can be optimized further for efficiency. Here are a few suggestions:
- Chunk size adjustment: Adjust the chunk size and overlap to balance performance and retrieval quality.
- Smaller model versions: Use smaller versions of DeepSeek-R1 (e.g., 7B, 8B, or 14B) via Ollama if the full model is too resource-heavy.
- Scale using Faiss: For larger documents, consider integrating Faiss for faster retrieval.
- Batch processing: Batch the chunks to improve embedding generation efficiency.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we built a RAG-based local chatbot using DeepSeek-R1 and Chroma for retrieval, ensuring accurate, contextually rich answers to questions based on a large knowledge base. This approach combines the power of DeepSeek-R1 with the flexibility of Ollama and Gradio to create a robust and interactive AI application.
Learn more by reading the full guide on DataCamp.
Click here to read the full article.
Comments